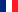
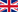
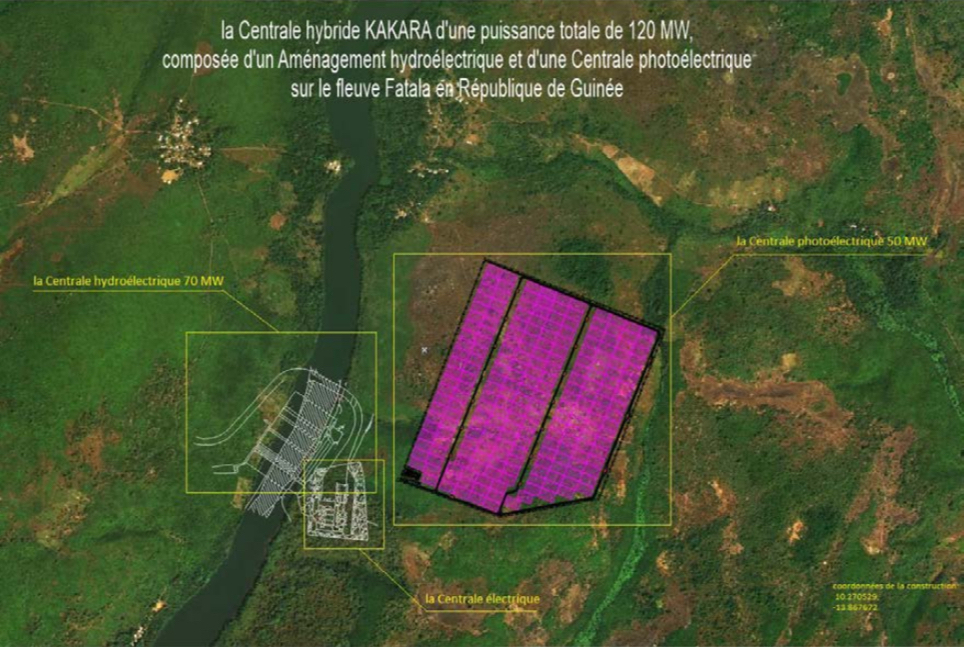
In a bold effort to address growing energy demands and promote sustainable development, Guinea has embarked on the construction of renewable energy plants, a significant step towards a cleaner and more inclusive energy future.
One of the most striking aspects of this initiative is the creation of thousands of jobs across the country. Renewable energy plant construction projects generate employment opportunities for specialized positions such as engineers and technicians, as well as jobs related to construction, maintenance, and facility operations. This surge in employment not only helps boost the local economy but also provides sustainable career prospects for many Guineans.
The positive social impact extends beyond job creation. With the expansion of energy capacity through these plants, tens of thousands of residents who were previously deprived of reliable access to electricity will benefit from this major advancement. Rural areas, often the farthest from traditional power grids, will see their communities illuminated, thereby improving the quality of life for inhabitants.
These renewable energy plants, particularly those utilizing hydroelectric and photovoltaic technologies, offer a sustainable solution to meet the country's energy needs. By harnessing Guinea's abundant natural resources, these projects not only provide clean electricity but also contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, reinforcing the country's commitment to combating climate change.
The Guinean government, collaborating with international partners and specialized companies, is demonstrating its commitment to placing sustainable development at the core of its energy agenda. These plants are not just infrastructure; they are catalysts for positive change, fostering social, economic, and environmental inclusion.
In conclusion, the construction of renewable energy plants in Guinea is not just a breakthrough in the energy sector but a transformative opportunity. The creation of jobs and access to electricity for tens of thousands of residents pave the way for a brighter, more equitable, and sustainable future for Guinea.